-
MIT Maritime Consortium
A new international collaboration unites MIT and maritime industry leaders to develop nuclear propulsion technologies, alternative fuels, data-powered strategies for operation, and more.
READ MORE -
Building networks of data science talent
Through partnerships with organizations like BREIT in Peru, IDSS is upskilling hundreds of learners around the world in data science and machine learning.
READ MORE -
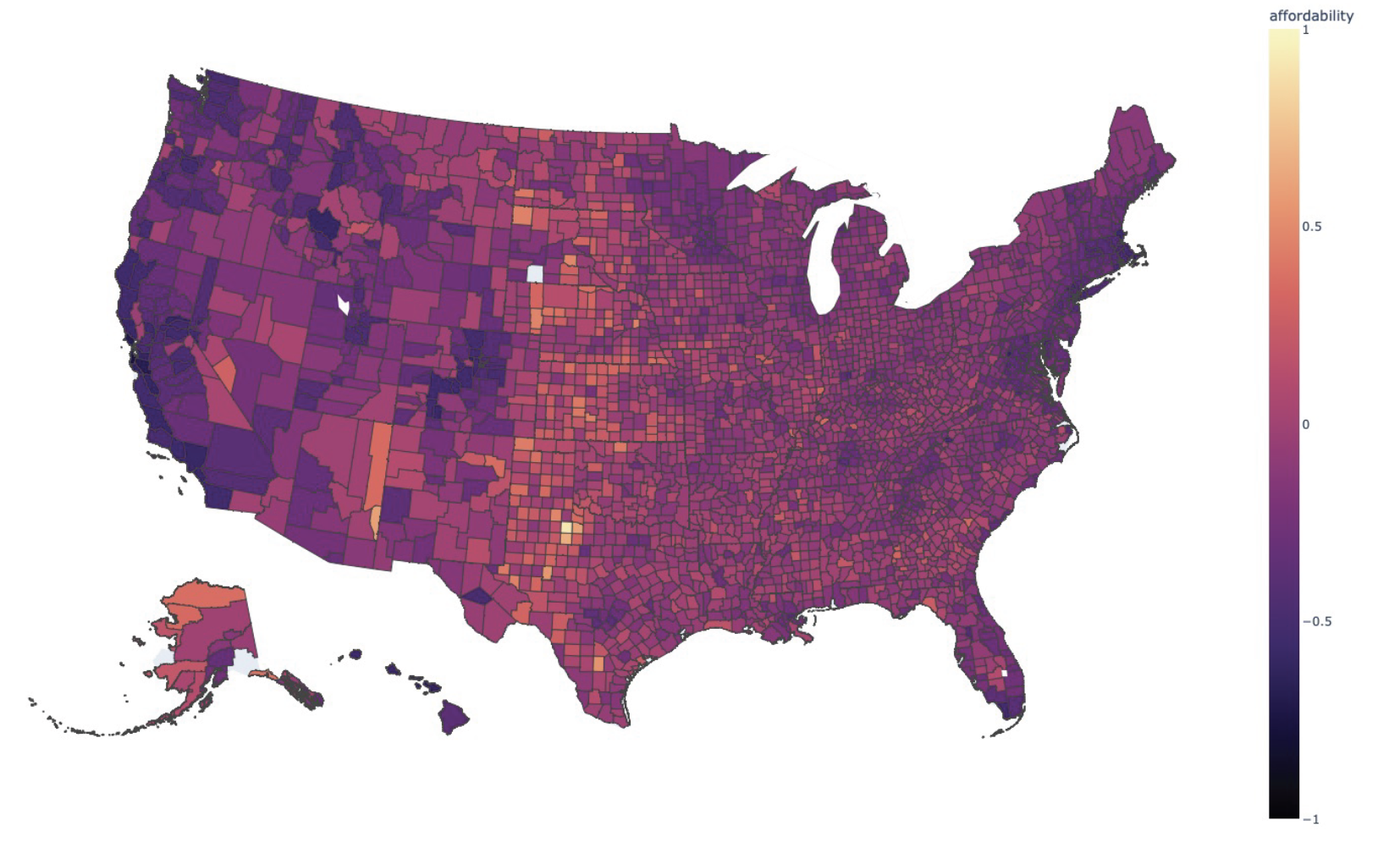
Who Can Afford to Buy a Home in America?
Owning a home is one of the most important ways of building wealth in America. As rises in home prices outpace rises in income, fewer and fewer Americans can afford to buy a home, causing the generational wealth gap to widen. Housing assistance programs are imperative to expand access to homeownership – particularly for Black Americans, who have historically been excluded from stable homeowning through policies and practices including redlining and exclusionary zoning. Designing effective housing assistance requires understanding where gaps in affordability currently exist for potential homeowners. Read more.
READ MORE -
Race-Neutral vs Race-Conscious: Using Algorithmic Methods to Evaluate the Reparative Potential of Housing Programs
The racial wealth gap in the US remains a persistent issue; white individuals possess six times more wealth than Black individuals. Leading scholars and public figures have pointed to slavery and post-slavery discrimination as root cause factors, and called for reparations. Yet the institutionalization of race-neutral ideologies in policies and practices hinders a reparative approach to closing the racial wealth gap. Read more.
READ MORE -
iBuyers and “Race for Profit”
iBuyers use automated valuation algorithms and streamlined home-buying processes, including exemption of repairs before selling and cash offers, to purchase homes. Previous literature has examined the roles and limitations of iBuyers in the housing market, but there is a lack of empirical research on the racial implications of these algorithmic home-buying processes. Using spatial lag model, this study identifies spatial clustering of iBuyer profit margins and a statistically significant and positive correlation between profit margins and the rise in the proportion of Black or Latinx residents within a given neighborhood tract. This work will be submitted to Journal of Urban Affairs. Read more.
READ MORE -
Studying the impact of police surveillance on racial bias using open data
Using data from 2000+ police departments, this project measures the effects of policing technologies, including face recognition, drones, body-worn cameras, predictive policing, and home security partnerships, on racial biases in law enforcement.
READ MORE -
The Police or the Public? 911 Calls and Racial Discriminations in Policing
A large proportion of police-citizen interactions are initiated by 911, and thus pairing 911 call data with police stop data provides a step toward a more systematic causal framework for estimating racial bias.
READ MORE -
Tradeoffs in Hotspot Predictive Policing
Predictive policing systems use narrowly scoped data and narrowly defined objectives that lead to 'hotspot' policing — disproportionate policing of small areas. What impact does this have on communities beyond how it effects crime? We examine how algorithms can lead to changes in police practices and policies.
READ MORE -
Understanding the Causal Effect of Race in the Criminal Justice System
Applying a systematic framework to causally understand the effect of race on policing, the policing team looks at linked data quantitatively to estimate how different races benefit or suffer differently from the same policy interventions.
READ MORE
Institute for Data, Systems, and Society (IDSS) is committed to addressing complex societal challenges by advancing education and research at the intersection of statistics, data science, information and decision systems, and social sciences.
News
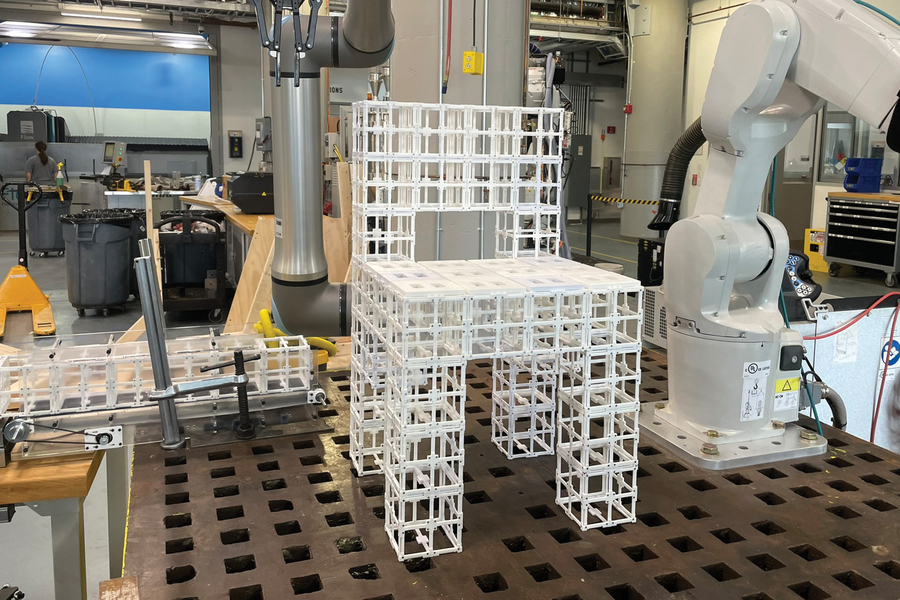
“Robot, make me a chair”
An AI-driven system developed by a team including IDSS faculty members Faez Ahmed and Lawrence Sass lets users design and build simple, multicomponent objects by describing them with words.

IDSS partners with Masai for Machine Learning in India
Online learners in the ‘Machine Learning with Python’ program will learn the foundations of ML and AI, from data handling to neural networks, with support from an IDSS Teaching Assistant.

Making clean energy investments more successful
Tools for forecasting and modeling technological improvements and the impacts of policy decisions can result in more effective and impactful decision-making, says recent article co-authored by IDSS faculty Jessika Trancik.